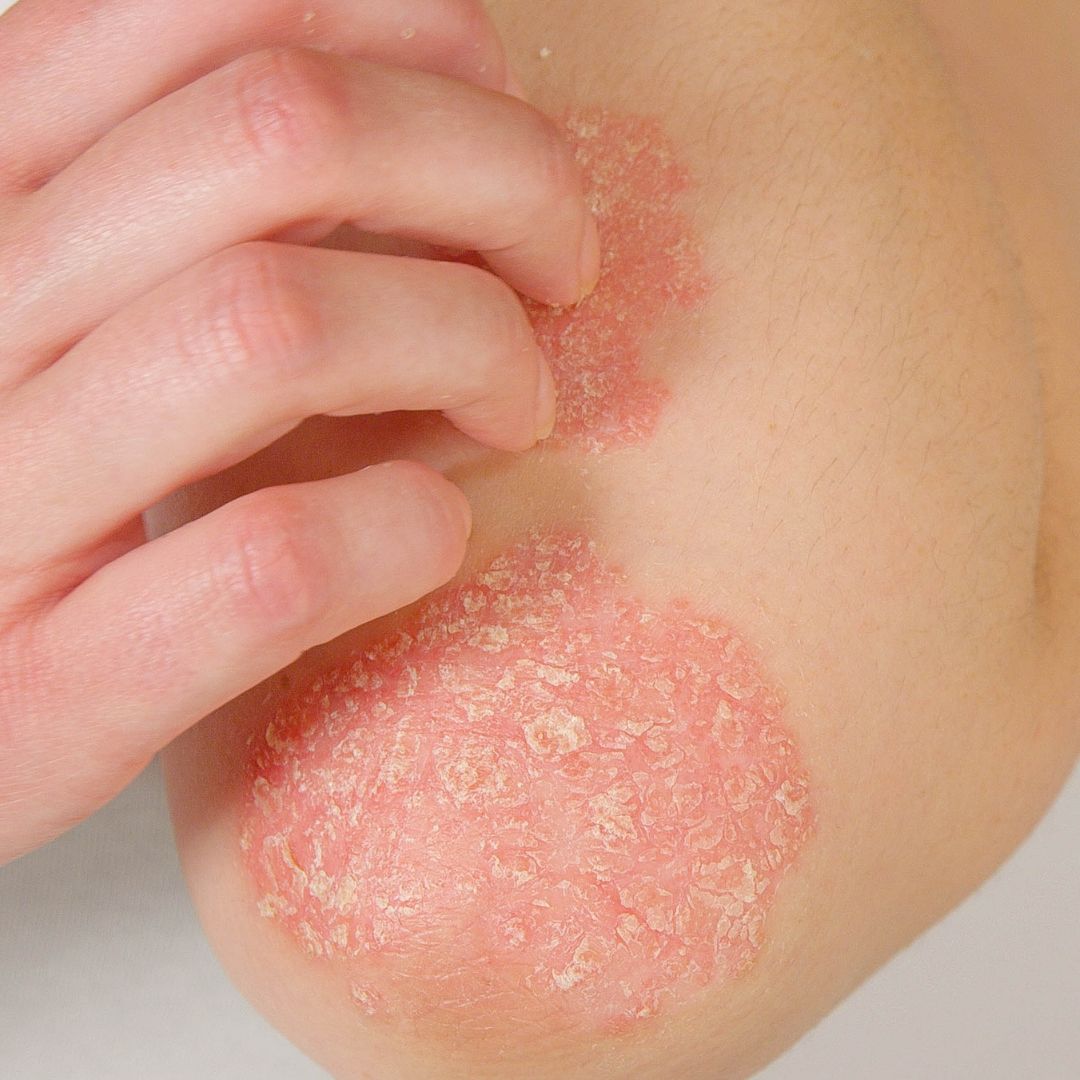
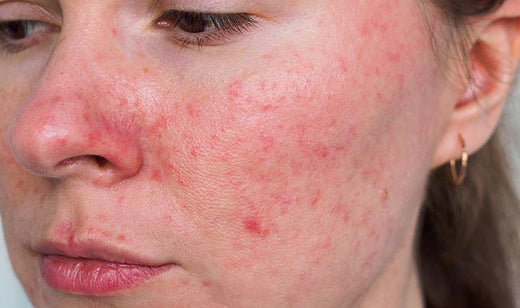
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterised by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, which can lead to discomfort, embarrassment, and even infection. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies for skin eczema, providing a comprehensive guide for those affected by this condition.
Causes of Eczema
While the exact cause of eczema is still unknown, research suggests that it is an interaction between genetic and environmental factors that leads to an overactive immune response. This response causes the skin barrier to become dry and itchy, leading to the characteristic symptoms of eczema.
- Genetic Component: A family history of eczema, allergies, and asthma can increase the risk of developing eczema.
- Environmental Triggers: Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and fragrances can trigger eczema, as can allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Stress: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms, and some people may experience eczema as a result of stress.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can vary in severity and location, but common symptoms include:
- Dry, itchy, and inflamed skin
- Redness and swelling
- Blisters and rashes
- Crusting and oozing
- Skin infections
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with its own set of symptoms and triggers. The most common types include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common type of eczema, characterized by dry, itchy skin and a family history of allergies and asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by skin contact with irritants or allergens, such as soaps, detergents, or metals.
- Nummular Eczema: Characterised by coin-shaped patches of dry, itchy skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: A type of eczema that affects the scalp, face, and other oily areas.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Caused by poor blood circulation, often affecting the lower legs.
Treatments for Eczema
While there is no cure for eczema, there are several treatments available to manage symptoms and prevent flares:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Creams, ointments, and lotions that reduce inflammation and itching.
- Moisturisers: Barrier repair moisturisers that lock in moisture and soothe dry skin.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to specific wavelengths of light to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Systemic Medications: Pills and injections that can be used for more severe cases.
- Biologics: Medications that target specific proteins in the immune system to reduce inflammation.
Prevention Strategies
While eczema is not contagious, there are several strategies that can help prevent flares and manage symptoms:
- Moisturise: Keeping the skin hydrated with gentle, fragrance-free moisturisers.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoiding harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances that can trigger eczema.
- Manage Stress: Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation and deep breathing.
- Wear Cool Clothing: Wearing smooth, breathable clothing to reduce irritation.
- Keep the Environment Clean: Keeping the home clean and dust-free to reduce exposure to allergens.
Conclusion
Eczema is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments, individuals can take control of their eczema and reduce the impact it has on their daily lives. With the right treatment plan and prevention strategies, it is possible to manage eczema and live a comfortable, confident life.